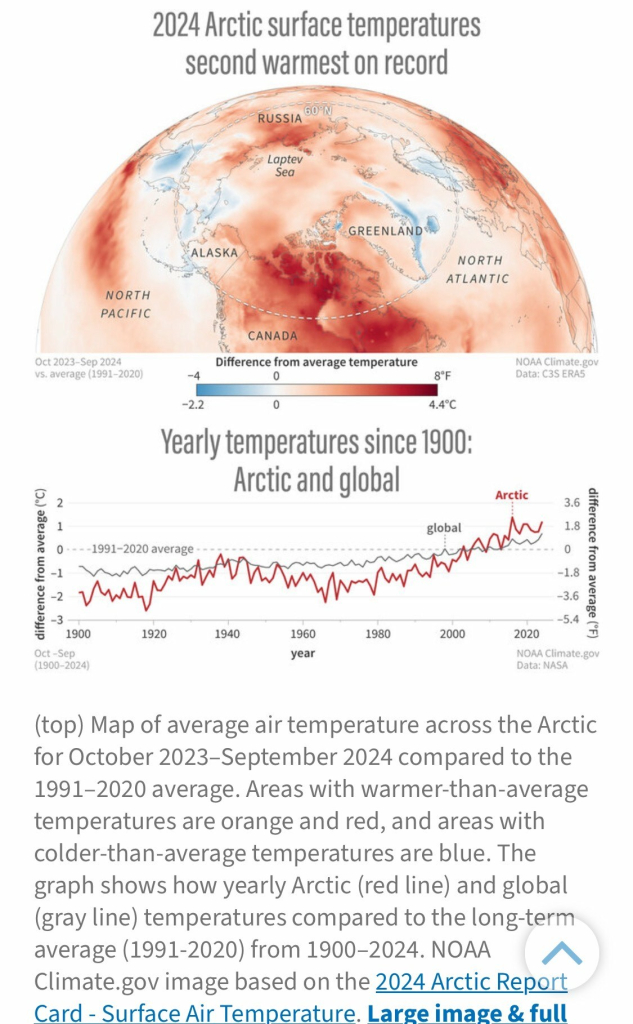
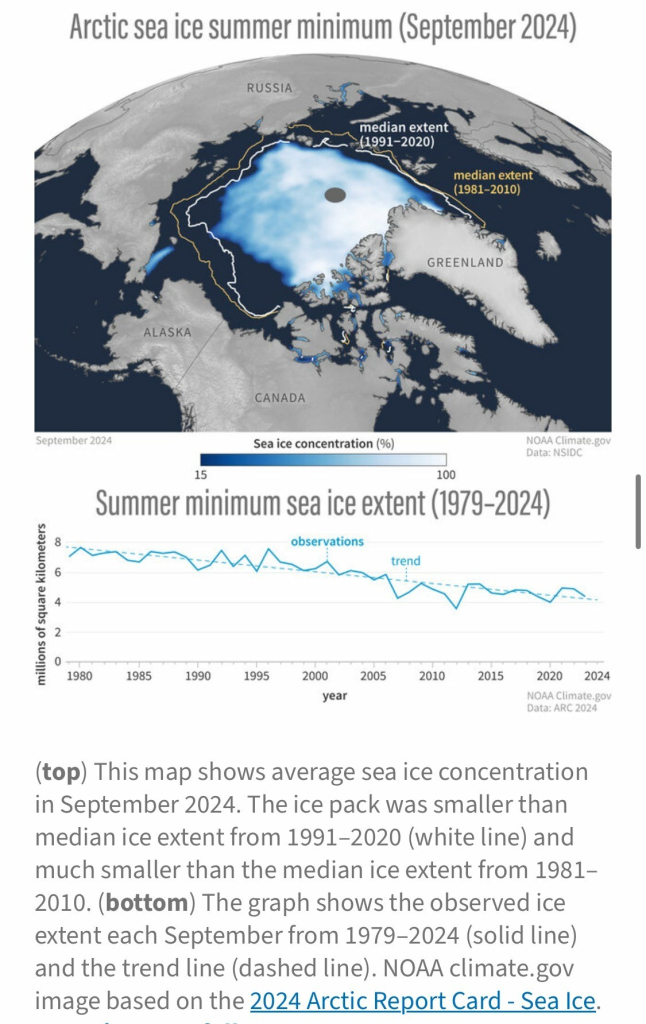
Wow—
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration ( #NOAA )called out a rapidly warming Arctic in December of last year.
“This year's report demonstrates the urgent need for adaptation as climate conditions quickly change.”
-and-
The arctic tundra is “now emitting more carbon that it stores... yet one more sign... of the consequences of inadequately reducing fossil fuel pollution.”
#climate #ClimateChange #USA #environment
https://www.climate.gov/news-features/understanding-climate/2024-arctic-report-card-documents-rapid-dramatic-change
(I archived the main page so far.)
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration ( #NOAA )called out a rapidly warming Arctic in December of last year.
“This year's report demonstrates the urgent need for adaptation as climate conditions quickly change.”
-and-
The arctic tundra is “now emitting more carbon that it stores... yet one more sign... of the consequences of inadequately reducing fossil fuel pollution.”
#climate #ClimateChange #USA #environment
https://www.climate.gov/news-features/understanding-climate/2024-arctic-report-card-documents-rapid-dramatic-change
(I archived the main page so far.)
2024 Arctic Report Card documents rapid, dramatic change
Among the changes, the Arctic tundra is now releasing more carbon dioxide to the atmosphere than it stores.NOAA Climate.gov
Dieser Beitrag wurde bearbeitet. (4 Tage her)