Suche
Beiträge, die mit ancientegypt getaggt sind
"2020
I may not have found the answer to the Secret I was looking for in Kemet, but I shared something with the thousand-year-old lords of the Nile. Then, I remembered this passage from a story that some Bards once told:
[...] Tell me why I had to be a Powerslave
I don't wanna die, I'm a god
Why can't I live on?
When the Life Giver dies
All around is laid waste
And in my last hour
I'm a Slave to the Power of Death [...]
(Iron Maiden, 1984, Powerslave)"
[Excerpt from the Sukha' SacredBrew Logbook]
#egyptphotography #desertnature #abusimbel #abusimbeltemple #egypt #ancientegypt #aswan #aswanegypt #nineteenthdynastyofegypt #newkingdom #ramessesii #ramessesthegreat #upperegypt #microblog #blogging #blog #storytelling #storytime #travel #travelphotography #travelblogger #travelfed
I may not have found the answer to the Secret I was looking for in Kemet, but I shared something with the thousand-year-old lords of the Nile. Then, I remembered this passage from a story that some Bards once told:
[...] Tell me why I had to be a Powerslave
I don't wanna die, I'm a god
Why can't I live on?
When the Life Giver dies
All around is laid waste
And in my last hour
I'm a Slave to the Power of Death [...]
(Iron Maiden, 1984, Powerslave)"
[Excerpt from the Sukha' SacredBrew Logbook]
#egyptphotography #desertnature #abusimbel #abusimbeltemple #egypt #ancientegypt #aswan #aswanegypt #nineteenthdynastyofegypt #newkingdom #ramessesii #ramessesthegreat #upperegypt #microblog #blogging #blog #storytelling #storytime #travel #travelphotography #travelblogger #travelfed
Marriage in #AncientEgypt
In ancient Egypt, it is believed that “most marriages were arranged, with an eye to social and financial advantages” (Watterson, 15).
Most Egyptian men had one wife, although men of higher status could take on other wives or concubines “with the agreement of the spouse” (Watterson, 16).
Marriage was considered a legal contract, drawn up by the “prospective husband and the bride’s father” (Watterson, 15), but often the bride was the “contracting partner (Watterson, 16) and represented her own interests.
Women were allowed to initiate divorce and “often came out of the marriage with more security than many modern women” (Watterson, 16).
If a man initiated the divorce, he “had to return her dowry, give her the marriage gift […] and pay her compensation” (Watterson, 16). If the woman initiated the divorce, she “was given back her dowry and usually a share of any property” (Watterson, 16) acquired after the marriage.
Both “parties were free to remarry” (Watterson, 16) after the divorce.
#WomensRights #Autonomy
#LegalStatus #Histodon #AncientHistory
In ancient Egypt, it is believed that “most marriages were arranged, with an eye to social and financial advantages” (Watterson, 15).
Most Egyptian men had one wife, although men of higher status could take on other wives or concubines “with the agreement of the spouse” (Watterson, 16).
Marriage was considered a legal contract, drawn up by the “prospective husband and the bride’s father” (Watterson, 15), but often the bride was the “contracting partner (Watterson, 16) and represented her own interests.
Women were allowed to initiate divorce and “often came out of the marriage with more security than many modern women” (Watterson, 16).
If a man initiated the divorce, he “had to return her dowry, give her the marriage gift […] and pay her compensation” (Watterson, 16). If the woman initiated the divorce, she “was given back her dowry and usually a share of any property” (Watterson, 16) acquired after the marriage.
Both “parties were free to remarry” (Watterson, 16) after the divorce.
#WomensRights #Autonomy
#LegalStatus #Histodon #AncientHistory
[Thread] So, the following is from a presentation I gave at a Women and Gender Studies class I took in 2017 (as a Classics Major). I thought it was important to post here -- especially in this day and age where women's reproductive rights are being threatened. In some ways, we've taken a step backward as time has gone on...
#ReproductiveRights #WomensRights #AncientEgypt #AncientGreece #AncientRome #Abortion #BirthControl #Autonomy #Professions #Education #LegalStatus #Histodon #AncientHistory
#ReproductiveRights #WomensRights #AncientEgypt #AncientGreece #AncientRome #Abortion #BirthControl #Autonomy #Professions #Education #LegalStatus #Histodon #AncientHistory
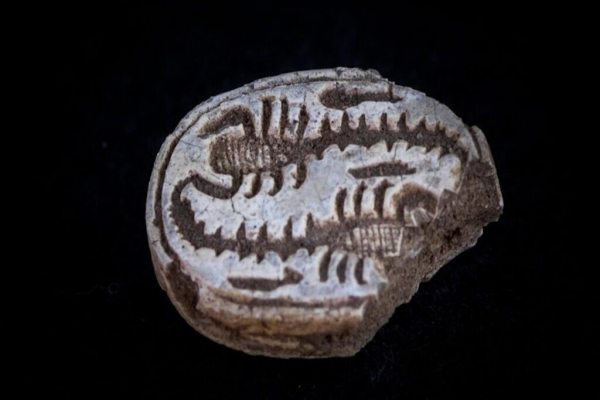
12-Year-Old Girl Discovers 3,500-Year-Old Egyptian Amulet While Hiking https://www.byteseu.com/532322/ #AncientEgypt #Archaeology #DungBeetles #Egypt #Israel #Scarabs
12-Year-Old Girl Discovers 3,500-Year-Old Egyptian Amulet While Hiking
Imagine finding a pebble and discovering it’s actually a 3,500-year-old artifact. That’s exactly what happened to a young girl in Israel, who suspected her find was special even before she and her mother sought expert advice.BYTESEU (Bytes Europe)
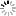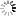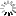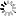


![Text:
Marriage in Ancient Egypt (cont'd)
Women were allowed to initiate divorce and “often came out of the marriage with more security than many modern women” (Watterson, 16).
If a man initiated the divorce, he “had to return her dowry, give her the marriage gift […] and pay her compensation” (Watterson, 16). If the woman initiated the divorce, she “was given back her dowry and usually a share of any property” (Watterson, 16) acquired after the marriage.
Both “parties were free to remarry” (Watterson, 16) after the divorce.
Text:
Marriage in Ancient Egypt (cont'd)
Women were allowed to initiate divorce and “often came out of the marriage with more security than many modern women” (Watterson, 16).
If a man initiated the divorce, he “had to return her dowry, give her the marriage gift […] and pay her compensation” (Watterson, 16). If the woman initiated the divorce, she “was given back her dowry and usually a share of any property” (Watterson, 16) acquired after the marriage.
Both “parties were free to remarry” (Watterson, 16) after the divorce.](https://friendica-leipzig.de/photo/preview/600/668548)


