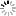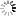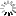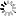Suche
Beiträge, die mit pumakit getaggt sind
New stealthy Pumakit Linux Rootkit Malware spotted in the Wild. 
IT-security researchers have uncovered a new Linux rootkit called PUMAKIT that comes with capabilities to escalate privileges, hide files & directories, and conceal itself from system tools, while simultaneously evading detection.
https://www.elastic.co/security-labs/declawing-pumakit
#linux #pumakit #malware #it #security #privacy #engineer #media #tech #news

IT-security researchers have uncovered a new Linux rootkit called PUMAKIT that comes with capabilities to escalate privileges, hide files & directories, and conceal itself from system tools, while simultaneously evading detection.
https://www.elastic.co/security-labs/declawing-pumakit
#linux #pumakit #malware #it #security #privacy #engineer #media #tech #news
Declawing PUMAKIT — Elastic Security Labs
PUMAKIT is a sophisticated loadable kernel module (LKM) rootkit that employs advanced stealth mechanisms to hide its presence and maintain communication with command-and-control servers.www.elastic.co

![[ImageSource: Elastic Security]
Pumakit Infection Chain.
Pumakit employs a multi-stage infection process starting with a dropper named 'cron,' which executes embedded payloads ('/memfd:tgt' and '/memfd:wpn') entirely from memory.
The '/memfd:wpn' payload, which executes in a child process, performs environment checks and kernel image manipulation and eventually deploys the LKM rootkit module ('puma.ko') into the system kernel.
Embedded within the LKM rootkit is Kitsune SO ('lib64/libs.so'), acting as the userland rootkit that injects itself into processes using 'LD_PRELOAD' to intercept system calls at the user level. [ImageSource: Elastic Security]
Pumakit Infection Chain.
Pumakit employs a multi-stage infection process starting with a dropper named 'cron,' which executes embedded payloads ('/memfd:tgt' and '/memfd:wpn') entirely from memory.
The '/memfd:wpn' payload, which executes in a child process, performs environment checks and kernel image manipulation and eventually deploys the LKM rootkit module ('puma.ko') into the system kernel.
Embedded within the LKM rootkit is Kitsune SO ('lib64/libs.so'), acting as the userland rootkit that injects itself into processes using 'LD_PRELOAD' to intercept system calls at the user level.](https://friendica-leipzig.de/photo/preview/600/367019)
![[ImageSource: Elastic Security]
Pumakit using ftrace to hook Syscalls.
The malware uses the internal Linux function tracer (ftrace) to hook into as many as 18 different system calls and various kernel functions such as "prepare_creds," and "commit_creds" to alter core system behaviors and accomplish its goals.
<https://www.kernel.org/doc/html/latest/trace/ftrace.html>
"Unique methods are used to interact with Pumakid, including using the rmdir() syscall for privilege escalation and specialized commands for extracting configuration and runtime information," the researchers said. [ImageSource: Elastic Security]
Pumakit using ftrace to hook Syscalls.
The malware uses the internal Linux function tracer (ftrace) to hook into as many as 18 different system calls and various kernel functions such as "prepare_creds," and "commit_creds" to alter core system behaviors and accomplish its goals.
<https://www.kernel.org/doc/html/latest/trace/ftrace.html>
"Unique methods are used to interact with Pumakid, including using the rmdir() syscall for privilege escalation and specialized commands for extracting configuration and runtime information," the researchers said.](https://friendica-leipzig.de/photo/preview/600/367021)