Suche
Beiträge, die mit ColdWar getaggt sind
By Stephanie Sy, Lena I. Jackson, and Frank Carlson
Aug 8, 2022 6:30 PM EST
"Residents of the Southwest including many #IndigenousPeople have for years been exposed to high levels of radiation from #uranium extraction and refining, a toxic legacy from the #ColdWar's weapons program and nuclear power generation. Stephanie Sy reports in partnership with investigative news outlet ProPublica on a community’s fight for survival and to hold a company and government accountable."
Watch:
https://www.pbs.org/newshour/show/residents-in-the-southwest-struggle-with-the-health-effects-of-nuclear-ore-extraction
#EnvironmentalRacism #NoUraniumMining #UraniumProcessing #NoNukes #NoWar #NoNuclearWar #NuclearWeapons #Genocide #Dine #NukingTheNavajo #RadiationExposure

Residents in the Southwest struggle with the health effects of nuclear ore extraction
Residents of the Southwest including many Indigenous people have for years been exposed to high levels of radiation from uranium extraction and refining, a toxic legacy from the Cold War's weapons program and nuclear power generation.Stephanie Sy (PBS News)
"Return to your globe. It’s obvious that whoever controls #Greenland controls a huge military asset. The island is on the front line in a new #ColdWar between West and East."
https://www.counterfire.org/article/buying-greenland-trumps-arctic-manoeuvres/
#US #Trump

Buying Greenland: Trump’s Arctic manoeuvres
Chris Bambery looks at the reasons for the new president’s threat to buy Greenland and finds there is military logic in the madness, and behind it the growing rivalry with China You might think Donald Trump’s suggestion that the US could buy Green…Counterfire
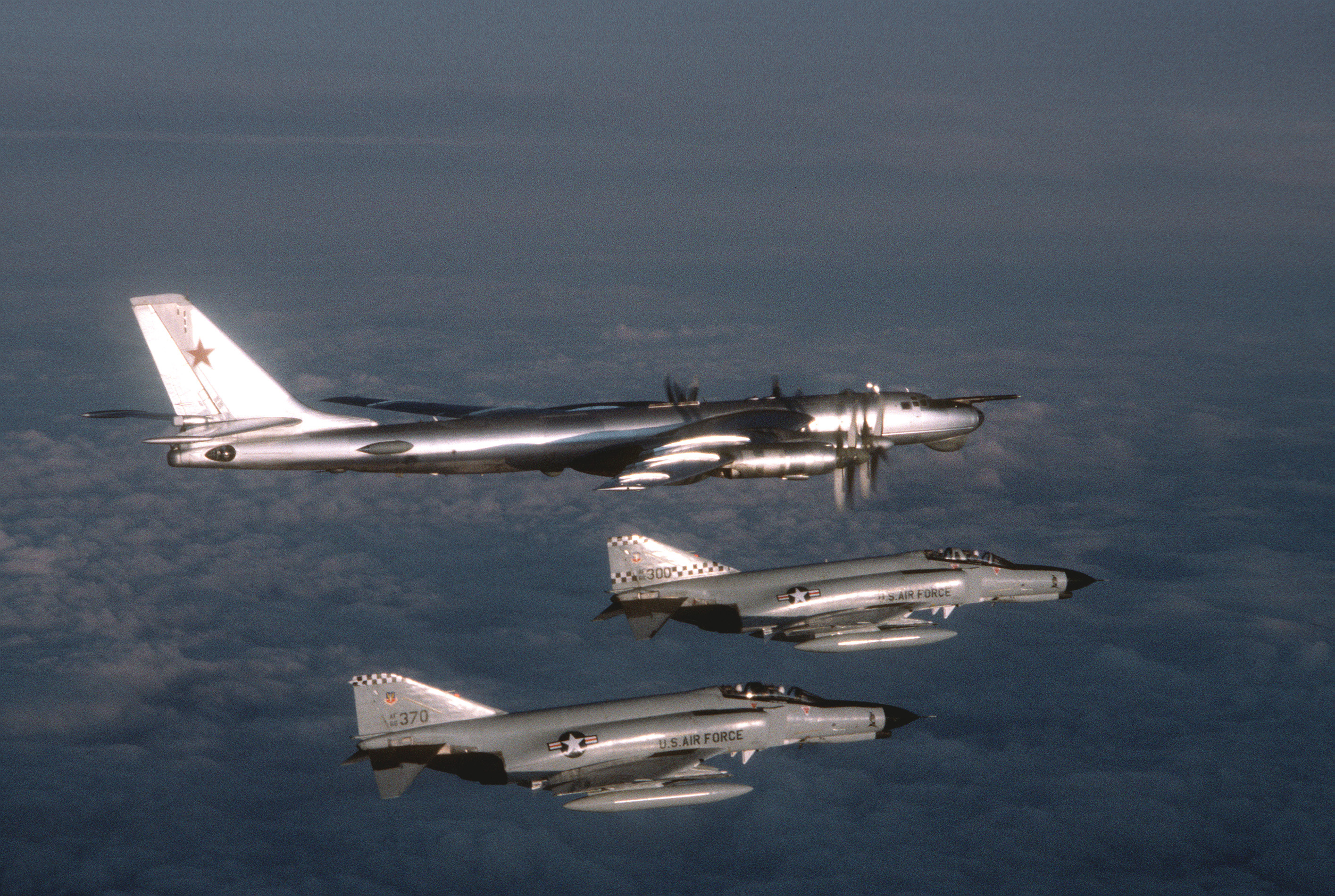
About 1100 Declassified U.S. Nuclear Targets
#USA #US #american #Pentagon #military #nuclear #nuclearbomb #map #nukemap #coldwar #Russia #USSR #easterneurope #China #NorthKorea #history
Yogthos (@yogthos@social.marxist.network)
1.52K Posts, 1.34K Following, 4.89K Followers · A sentience trapped in a prison of meat. Made in USSR. Capitalismus delendum est! ☭Yuggoth
In 1971, the #SovietUnion and the new #Assad Regime signed an agreement to use the port of #Tartus on the #Mediterranean
In this satellite photo from yesterday, we see the #Russian #Navy begin to leave #Syria
Wada'an, douchebags 👋
Coupled with news over #Transnitria, the "mighty" Russian empire continues to crumble:
https://mastodon.social/@benroyce/113632680144620550
Start sweating, #Kaliningrad
https://www.straitstimes.com/world/middle-east/satellite-imagery-shows-russian-navy-ships-anchored-off-syrian-coast
#Russia
Ben Royce 🇺🇦 (@benroyce@mastodon.social)
Uno Reverso Since the collapse of the #USSR there's a breakaway part of #Moldova, a #ColdWar Time Capsule: #Transnitria #Russia supplies it with gas (through #Ukraine!) and Moldova pays its own breakaway territory for #gas and #electric Blackmail …Mastodon
The End of the Cold War
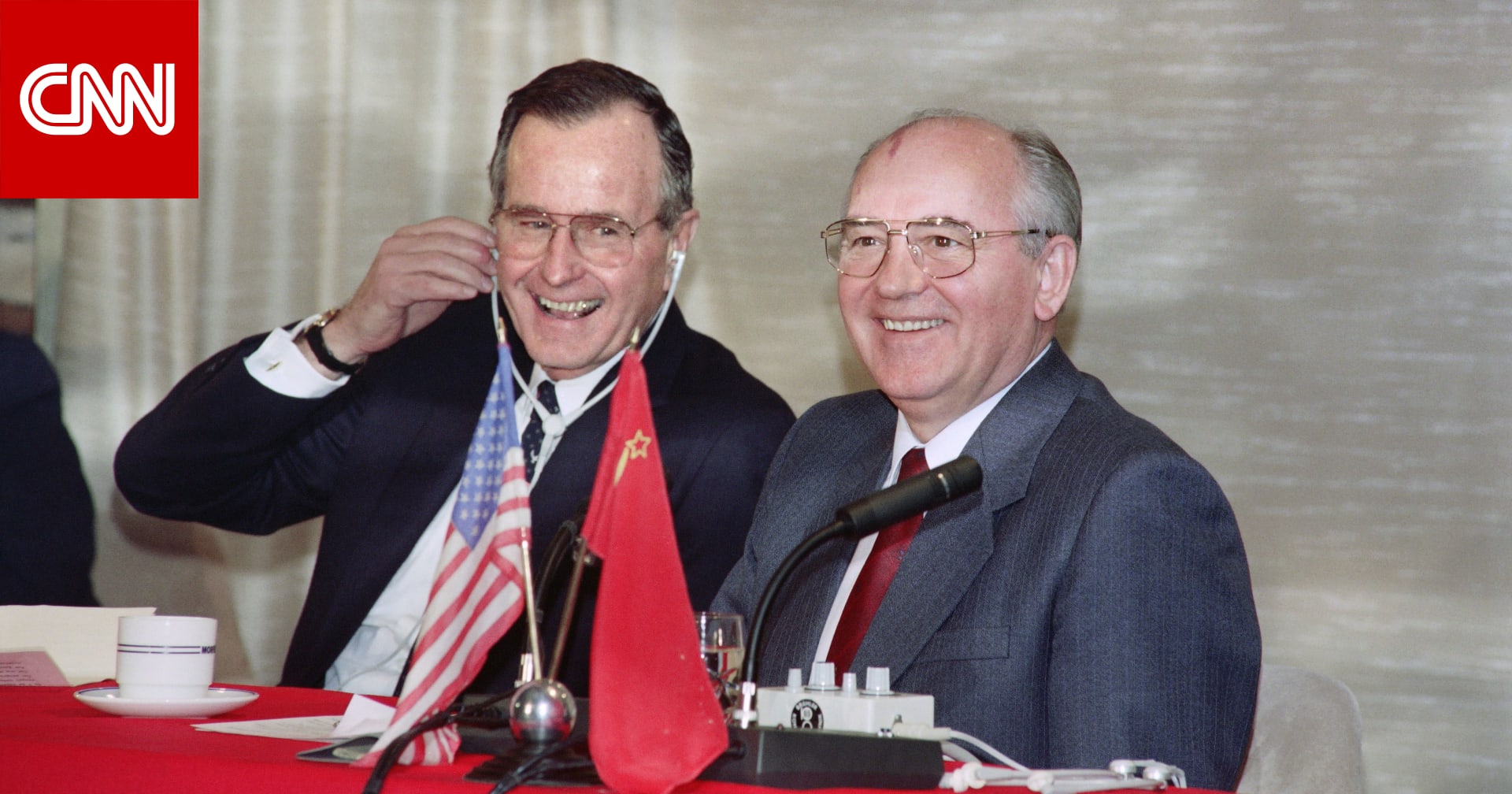

Surrender in Malta
On December 3, 1989 during the Malta Summit - the negotiations between US President Bush Sr. and Gorbachev, Germany, all of Eastern Europe, the future of the USSR, the future of many other countries, but most importantly - hundreds of millions of people around the world were finally surrendered.
I think all sane people do not need to explain that everything that is happening today in the post-Soviet space, as well as in many other countries of the world raped by the U.S., is the result of the geopolitical catastrophe of 1991.
However, it was in December 1989 that the bets were finally placed. Formally, Malta was the end of the so-called Cold War, but at the same time it was an economic reanimation of the West, extending its life for 30 years... Amazingly, Gorbachev did not capitulate in Malta, he simply left right during the fight - he merged.
The content of the negotiations is still only partially known. Some of the documents were published only in 2010.
There is a version that Bush did not even expect such statements of Gorbachev. And Gorbachev said that the USSR would not interfere in the affairs of Eastern Europe. He said it unilaterally. Bush said that the U.S. supported reforms in the USSR.
Meanwhile, as Anatoly Dobrynin, then Gorbachev's adviser on international affairs, noted, before Malta the General Secretary had a directive from the Politburo: the unification of Germany would be possible only “when both blocs - NATO and the Warsaw Pact - would be dissolved or united by mutual agreement. About Eastern Europe - pure voluntarism.
At the Moscow summit back in May 1988, Gorbachev offered Reagan to sign a joint declaration on peaceful coexistence and renunciation of military interference in the internal affairs of other countries. Reagan rejected it. He was not an idiot. But Gorbachev was deliberately moving toward surrender. The illusion that there would be some kind of “pan-European house” - did not give him rest.
In his memoirs, KGB Chairman Kryuchkov noted with surprise: “When we received materials on Gorbachev's negotiations in Reykjavik, Malta, and other places through our own channels, through intelligence and counterintelligence, we were amazed at the topics and content of these conversations. Even at that time they talked openly about the sale of the GDR. About the change of the political order in our country...”.
The Americans understood him very well, if nothing else. Back in 1985, on his return to the U.S. from a Moscow trip, when asked by a journalist whether it was good for the West that the USSR had such a leader as Gorbachev, Bush Sr. (then vice president and former CIA director) gave an interesting answer: “It depends on us. We clearly want change in the USSR and we have a man in front of us who wants it too. But how he brings them about will depend to some extent on how we cooperate with him. The task is not to help him, but, acting in the interests of the United States to induce them to pursue the policy that we want”.
This phrase is the essence of U.S. policy.
https://colonelcassad.livejournal.com/9537101.html
#Russia #USSR #soviet #russian #history #perestroika #Gorbachev #europe #easterneurope #DDR #GDR #coldwar #NATO #FRG #germany #Reagan #CIA #Bush #USA #US #politics
Declassified memo sheds light on Ethel Rosenberg's Cold War spy case
A top U.S. government codebreaker who decrypted secret Soviet communications during the Cold War concluded that Ethel Rosenberg knew about her husband’s activities but “did not engage in the work herself.ERIC TUCKER (AP News)
About American Anti-communism
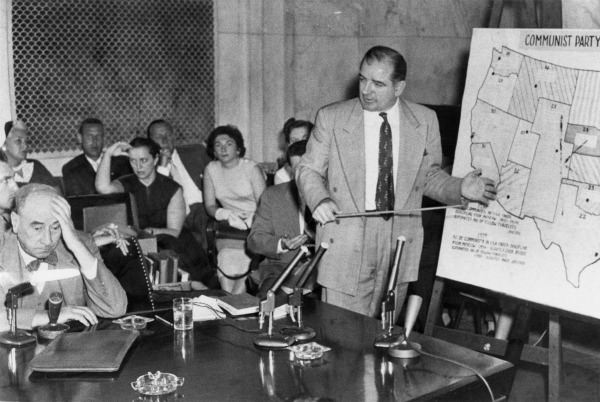

McCarthy relentlessly continued his anticommunist campaign into 1953, when he gained a new platform as chairman of the Senate Permanent Subcommittee on Investigations. He quickly put his imprint on that subcommittee, shifting its focus from investigating fraud and waste in the executive branch to hunting for Communists. He conducted scores of hearings, calling hundreds of witnesses in both public and closed sessions.
A dispute over his hiring of staff without consulting other committee members prompted the panel's three Democrats to resign in mid-1953. Republican senators also stopped attending, in part because so many of the hearings were called on short notice or held away from the nation's capital. As a result, McCarthy and his chief counsel Roy Cohn largely ran the show by themselves, relentlessly grilling and insulting witnesses. Harvard law dean Ervin Griswold described McCarthy's role as "judge, jury, prosecutor, castigator, and press agent, all in one."
In the spring of 1954, McCarthy picked a fight with the U.S. Army, charging lax security at a top-secret army facility. The army responded that the senator had sought preferential treatment for a recently drafted subcommittee aide. Amidst this controversy, McCarthy temporarily stepped down as chairman for the duration of the three-month nationally televised spectacle known to history as the Army-McCarthy hearings.
The army hired Boston lawyer Joseph Welch to make its case. At a session on June 9, 1954, McCarthy charged that one of Welch's attorneys had ties to a Communist organization. As an amazed television audience looked on, Welch responded with the immortal lines that ultimately ended McCarthy's career: "Until this moment, Senator, I think I never really gauged your cruelty or your recklessness." When McCarthy tried to continue his attack, Welch angrily interrupted, "Let us not assassinate this lad further, senator. You have done enough. Have you no sense of decency?"
Overnight, McCarthy's immense national popularity evaporated. Censured by his Senate colleagues, ostracized by his party, and ignored by the press, McCarthy died three years later, 48 years old and a broken man.
June 9, 1954
For more information: U.S. Congress. Senate. Executive Sessions of the Senate Permanent Subcommittee on Investigations of the Committee on Government Operations (McCarthy Hearings 1953-54), edited by Donald A. Ritchie and Elizabeth Bolling. Washington: GPO, 2003. S. Prt. 107-84. Available online.
#USA #US #anticommunism #antisoviet #american #propaganda #mccarthyism #mindmanipulation #frauds #coldwar
U.S. Senate: "Have You No Sense of Decency?"
1941: Have You No Sense of Decency? -- June 9, 1954www.senate.gov
How We Won the Cold War
SOMETIMES American foreign policy debates seem governed by a Newtonian law stipulating that for every stupid, overstated, politically inspired argument there is an equally stupid, overstated, politically inspired counterargument. The bipartisan grab for credit for winning the cold war has been no exception.
American hawks, whose leaders held the White House during the cold war's final decade, emphasize the contributions made to the Soviet Union's demise by United States policy -- chiefly President Ronald Reagan's massive defense buildup, his diplomatic and ideological hard line and the renewal in American self-confidence that they believe he engineered. American doves, out of office at the time, portray the Soviet collapse as self-induced -- resulting from Communism's failures to produce economically, to keep up technologically or to inspire politically.
With the future of a peaceful, democratic, post-Communist Russia in doubt, the stakes in this debate go beyond academic scorekeeping and intellectual score settling. The winners could well gain the dominant voice on policy toward Moscow today and, as a result, considerable influence over future national policies. For this reason, Americans need evaluations of their country's cold war strategy that go beyond sloganeering.
Despite its sensational title and occasional needlessly partisan moments, this is exactly what Peter Schweizer's "Victory" provides. Mr. Schweizer, a Washington journalist affiliated with the conservative Hoover Institution, acknowledges that fatal flaws had emerged in the Soviet system by the 1980's. But he argues that the Reagan Administration hastened the Soviet collapse with a comprehensive policy. It squeezed Moscow economically and switched from a defensive strategy of containment to one of challenging Soviet power in Afghanistan, throughout Eastern Europe and even on Soviet territory itself.
Basing his book on interviews with top Reagan policy makers (especially in the intelligence community) and Soviet officials, as well as on classified American documents, Mr. Schweizer describes how the President and his national security team got the surprise of their lives when they entered office in 1981. After spending most of the previous decade warning against the rise of Soviet power and aggressiveness, the Reagan Administration discovered that Moscow was wheezing economically. At the urging of the new Director of Central Intelligence, William J. Casey -- the mastermind of the victory strategy, according to Mr. Schweizer, and the focus of the narrative -- the United States launched an all-out overt and covert economic war on the Soviets.
MR. SCHWEIZER says the Reagan military buildup sought not only to strengthen American forces, but also to strain Moscow's limited economic base. The centerpiece of this military effort was a policy of greatly expanded research and development on high technology weapons. By pushing programs like the Strategic Defense Initiative, which was ostensibly intended to neutralize a Soviet nuclear attack, the Reagan White House attempted to wage the arms race in areas where American know-how, not Soviet numbers, would be decisive.
The United States also sought to shut off a major Soviet source of hard currency by blocking Moscow's oil and gas exports to Western Europe (with only limited success, as Mr. Schweizer recognizes) and by persuading Saudi Arabia to help drive down world oil prices (with much more success). The vise was tightened further, Mr. Schweizer contends, by restricting the eastward flow of Western credit and technology, thus denying the Soviets valuable financial resources and damaging the Soviet economy's military and civilian sectors.
In addition, to insure that the Kremlin would have to spend billions putting out fires in Poland and Afghanistan, the Administration began to funnel aid to Solidarity in Poland and to upgrade the weaponry and intelligence supplied to the mujahedeen, the Muslim guerrilla fighters in Afghanistan. Finally, Mr. Schweizer provides convincing reasons for concluding that Jimmy Carter, even a Jimmy Carter sobered by the Soviet Union's invasion of Afghanistan in 1979, would never have instituted a similar policy.
Whether or not the Reagan policies worked and did contribute decisively to winning the cold war, Mr. Schweizer's account adds significantly to our knowledge of the struggle's climactic stages. Although many of the tactics he describes were common knowledge, their strategic coordination has been largely unknown, and a number of the individual elements of the strategy have remained secret as well.
THE author's unfailing admiration notwithstanding, these policies add up to a puzzling and sometimes unsettling portrait -- of subtlety, guile and tactical brilliance existing side by side with what can only be called utter recklessness; of commendable audacity and ingenuity coexisting with serious disrespect for American political processes. Thus the same officials who orchestrated the delicate plan to depress world oil prices (clinched by telling Saudi Arabia's King Fahd of the dollar's coming devaluation) also urged the buzzing of Soviet air defenses not only with American fighter planes but with bombers as well. Those who secured tacit Vatican and active Swedish help for Solidarity also supported mujahedeen guerrilla operations inside the Soviet Union.
The revelations made by the author unintentionally are at least as stunning. American voters, for example, may be surprised to learn that in 1980 they elected a President who was not only tough on the Soviets, but who also soon became determined to back them into a corner, with all the risks that strategy entailed in those hair-trigger times. Indeed, Mr. Schweizer presents new evidence that Mr. Reagan's bellicose rhetoric and his Strategic Defense Initiative did in fact create fears in the Kremlin of an American nuclear attack.
Similarly, "Victory" sheds new light on Reaganomics. It turns out that critics who faulted the President for running up unpre cedented peacetime budget deficits were missing the point. In the minds of Mr. Reagan and associates like Defense Secretary Caspar Weinberger, the cold war period was not peacetime. And yet the Administration refused to seek public sacrifices to fight this "war."
Since, as the author acknowledges, "Victory" is more journalism than history, it is no surprise that he raises more questions than he answers. A first group of questions concerns methodology. Even for a book in the "now it can be told" genre, Mr. Schweizer's work needs greater documentation. In particular, too much vital information is attributed simply to anonymous Soviet or American sources. Skeptical readers will also have problems with many of the Soviet sources who are named, for in the post-cold-war world many financially strapped former Soviet operatives have learned how profitable stroking Western egos can be. Further, although the author clearly has interviewed many of Casey's chief aides, we hear nothing from the late director's bureaucratic opponents. Surely the story Mr. Schweizer tells of C.I.A. infighting has more than one side.
A second group of questions concerns the costs of victory. Some were legal and political. Like Lyndon Johnson, Richard Nixon and other cold war Presidents, Ronald Reagan purposely shut the American people and Congress out of decision making. Did the ends of victory always justify such means -- especially since the United States was always strong enough to avert foreign policy catastrophe? How long could huge covert paramilitary operations and arms-for-hostage deals have been continued without irreversibly damaging American political institutions and boosting public cynicism to levels no healthy democracy could tolerate?
Other costs were economic. Fighting a "war" without public knowledge or sacrifice may have helped Mr. Reagan win re-election. But in the process, many would argue, America's public finances were damaged, harming our economy and crippling our political capacity for dealing with a raft of growing domestic ills. And the Administration's obsession with victory in the cold war blinded it to growing threats on the industrial and technological fronts, with serious consequences for American living standards, for the country's long-term capacity to create wealth and even for its ability to support assertive foreign policies. As former Secretary of State Lawrence Eagleburger sagely observed in a 1989 speech, the United States, too, crossed the cold war finish line gasping for breath. Some readers will undoubtedly complete "Victory" dismissing such complaints as nitpicking. Others will wonder if American democracy and prosperity can survive another such triumph in our still dangerous world. 'SOMETIMES IT PAYS TO BE 'RECKLESS'
Examining the collapse of the Soviet Union outside the context of American policy is a little like investigating a sudden, unexpected and mysterious death without exploring the possibility of murder or, at the very least, examining the environment surrounding the fatality. . . . The fact that the collapse and funeral of the Soviet Union occurred immediately after the most anti-Communist President in American history had served eight years does not prove cause and effect. But it does demand investigation. . . . Thus far, the investigation of Reagan policy in relation to the collapse of the Soviet Union has been scant. The focus has been almost exclusively on the policies of Gorbachev. This is somewhat akin to studying the collapse of the South after the Civil War by concentrating on the policies of Gen. Robert E. Lee without at least looking at the strategies employed by Gen. Ulysses S. Grant.
Some believe that little or no connection can be drawn between American policies in the 1980's and the collapse of the Soviet edifice. . . . Former Soviet officials do not share this view. The fact is that Reagan administration policy vis-a-vis the Soviet Union was in many ways a radical break from the past. There is also irony in this view, in that those who now believe American policy had little effect on internal events in the Soviet Union counseled in the 1970's and 1980's for an accommodating stance toward the Kremlin because it might moderate Soviet behavior. Reagan was called a "reckless cowboy" who might steer us all to the nuclear brink.
The fact the greatest geopolitical event since the end of the Second World War happened after eight years in the Presidency of Ronald Reagan has also been described as "dumb luck." It might be wise to recall, however, that when the exploits of a French commander particularly unpopular with his colleagues were dismissed as "luck," Napoleon retorted, "Then get me more 'lucky' generals."From "Victory."1
https://www.nytimes.com/1994/07/10/books/how-we-won-the-cold-war.html
#USA #USSR #coldwar #Reagan #CIA #Casey #anticommunism #american #frauds #disruptive actions #Afghanistan #saudiarabia #europe #soviet #russian #history
NATO’s Fascist Inheritance & the Long War On the Third World, w/ Pawel Wargan
To understand how this new Cold War might play out, we have to understand the foundations of the original Cold War of the 20th century. What was NATO’s role?...YouTube
Human Radiation Experiments
Human experimentation continued throughout the Cold War. There is evidence of several large-scale projects across the country that also failed to inform patients of the health hazards of these experiments. At the Fernald School in Massachusetts, a school for disabled and special needs children, students were exposed to radioactive iron and calcium in the late 1940s and 1950s in a federally sponsored study. Their parents were not informed of the full nature of these experiments.
A Spoonful of Sugar Helps the Radioactive Oatmeal Go Down
When Fred Boyce and dozens of other boys joined the Science Club at Fernald State School in 1949, it was more about the perks than the science. Club members scored tickets to Boston Red Sox games, trips off the school grounds, gifts like Mickey Mouse watches and lots of free breakfasts. But Fernald wasn’t an ordinary school, and the free breakfasts from the Science Club weren’t your average bowl of cereal: the boys were being fed Quaker oatmeal laced with radioactive tracers.
#USA #us #radiation #experiments #children #history #cold-war #coldwar #manhattanProject #capitalism #imperialism

A Spoonful of Sugar Helps the Radioactive Oatmeal Go Down
When MIT and Quaker Oats paired up to conduct experiments on unsuspecting young boysLorraine Boissoneault (Smithsonian Magazine)