Suche
Beiträge, die mit Engineer getaggt sind

Google fixed two actively exploited Android zero-day flaws as part of its November security updates, addressing a total of 51 vulnerabilities. Tracked as CVE-2024-43047 & CVE-2024-43093, the two issues are marked as exploited in limited, targeted attacks.
https://source.android.com/docs/security/bulletin/2024-11-01
#google #android #update #zerodays #it #security #privacy #engineer #media #tech #news
A working Turing Machine was submitted to Lego Ideas, consisting of approximately 2,900 parts and a bucketload of extreme cleverness. The original machine was devised by mathematician Alan Turing in 1936. Turing's idea was a hypothetical system that could simulate any computer algorithm.
https://youtu.be/8AA3E05axHw?si=MWCSLoUNAxo2TiWD
#turing #machine #history #retro #computing #lego #artist #it #engineer #media #tech #art #news
Apple silicon Macs will get their ultimate gaming test. One of the most graphically demanding and visually impressive games in recent years, will soon get a Mac release, according to CD Projekt Red.
https://www.cyberpunk.net/en/news/50947/just-announced-cyberpunk-2077-ultimate-edition-coming-to-mac
#apple #silicon #mac #cyberpunk2077 #gaming #engineer #media #it #tech #news
Just Announced — Cyberpunk 2077: Ultimate Edition Coming to Mac!
Available early next year on Macs with Apple silicon, the Ultimate Edition will launch on the Mac App Store and Steam.Home of the Cyberpunk 2077 universe — games, anime & more
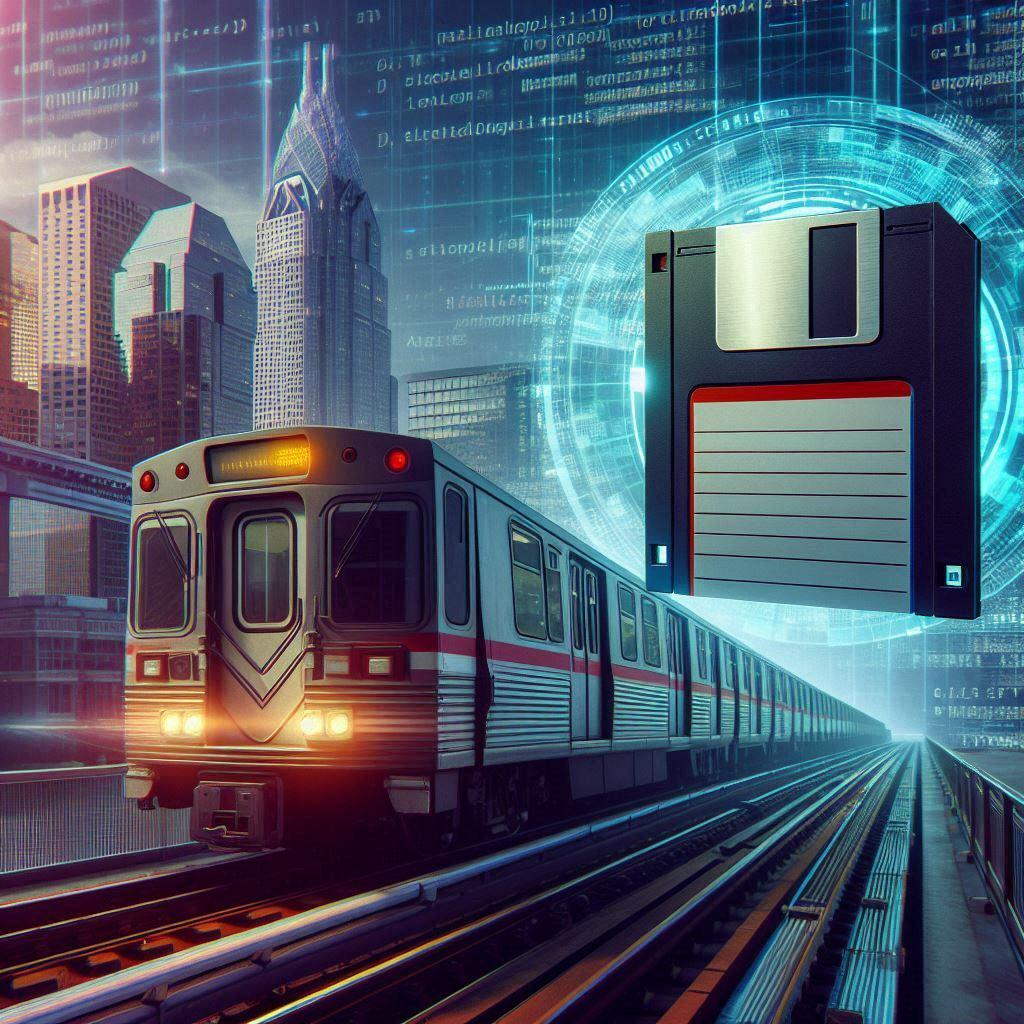
Yes, we're talking about the good old floppy disk, which is somehow still being utilized for something as important as a critical function of a public transport network within a major city’s.
https://www.govtech.com/transportation/s-f-muni-will-spend-212m-to-move-train-control-off-disk
#us #rail #train #control #metro #floppydisk #publictransport #travel #hitachirail #retrocomputing #engineer #media #tech #news
S.F. Muni Will Spend $212M to Move Train Control Off Disk
San Francisco’s Municipal Transportation Agency has approved a contract with Hitachi Rail for a new train control system. The replacement will move the Muni Metro off 1998 technology that runs on floppy disks.GovTech
The free version of the popular WordPress plugin LiteSpeed Cache has fixed a dangerous privilege elevation flaw on its latest release that could allow unauthenticated actors to gain admin rights.
[CVE-2024-50550 CVSS score: 8.1]
https://patchstack.com/articles/rare-case-of-privilege-escalation-patched-in-litespeed-cache-plugin/
#wordpress #litespeed #flaw #it #security #privacy #engineer #media #tech #news
Rare Case of Privilege Escalation Patched in LiteSpeed Cache Plugin - Patchstack
A vulnerability in LiteSpeed Cache allowed unauthorized admin access; fixed in version 6.5.2, with Patchstack users automatically protected.Rafie Muhammad (Patchstack)

Researchers have found new versions of a sophisticated Android financial-fraud Trojan that’s notable for its ability to intercept calls a victim tries to place to customer-support personnel of their banks.
https://www.zimperium.com/blog/mishing-in-motion-uncovering-the-evolving-functionality-of-fakecall-malware/
#android #fakecall #vishing #malware #it #security #privacy #engineer #media #tech #news
Mishing in Motion: Uncovering the Evolving Functionality of FakeCall Malware - Zimperium
In this blog post we share Zimperium’s Zero-Day Protection against the Water Makara Spear-Phishing campaign.Zimperium

The company also seeks to improve the system's security and has expanded its security bounty program to include rewards of up to [$1 Million] for vulnerabilities that could compromise “the fundamental security and privacy guarantees of PCC”.
https://security.apple.com/blog/pcc-security-research
#apple #pcc #vm #securityresearch #bug #bounty #programming #ai #it #security #privacy #engineer #media #tech #news

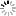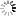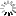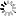
![[ImageSource: Bananaman 2018]
The design consisted of an infinitely long tape with symbols that could be moved left and right, a 'head' that could read the symbols and overwrite them with new ones, a finite control that described the machine's state, and a table to link each combination of state and symbol to an instruction for what to do next.
In addition to the constraints of making the device out of Lego, there was also the challenge of fitting into the limits imposed by Lego Ideas. At the time of submission, this was 3,000 parts and The Bananaman's contraption finally managed to come in at around 2,900. The limit has since been raised to 5,000 parts.
Fans of 3D printing will no doubt be pleased to note that some of the parts (notably one of the large gears) came from a printer, but only because buying missing bits online tends to take longer and cost more. A real-world version of the model was designed and built first to make sure it worked. [ImageSource: Bananaman 2018]
The design consisted of an infinitely long tape with symbols that could be moved left and right, a 'head' that could read the symbols and overwrite them with new ones, a finite control that described the machine's state, and a table to link each combination of state and symbol to an instruction for what to do next.
In addition to the constraints of making the device out of Lego, there was also the challenge of fitting into the limits imposed by Lego Ideas. At the time of submission, this was 3,000 parts and The Bananaman's contraption finally managed to come in at around 2,900. The limit has since been raised to 5,000 parts.
Fans of 3D printing will no doubt be pleased to note that some of the parts (notably one of the large gears) came from a printer, but only because buying missing bits online tends to take longer and cost more. A real-world version of the model was designed and built first to make sure it worked.](https://friendica-leipzig.de/photo/preview/600/254275)
![[ImageSource: 6zacl8.blogspot]
The original Alan Turing machine.
First demonstrated in 1950, this is one of Britain's earliest stored program computers and the oldest complete general purpose electronic computer in Britain. Designed and built at the National Physical Laboratory, Middlesex in 1949-1950, it was based on plans for a larger computer (the ACE) designed by the mathematician Alan Turing (1912-1954) at NPL between 1945 and 1947. Previously Turing worked on the Colossus computer used in codebreaking at Bletchley Park during World War II. Pilot ACE was estimated to have cost £50,000 to design and build, but by 1954 had earned over £240,000 from advanced scientific and engineering work in various fields including crystallography, aeronautics and computing bomb trajectories. [ImageSource: 6zacl8.blogspot]
The original Alan Turing machine.
First demonstrated in 1950, this is one of Britain's earliest stored program computers and the oldest complete general purpose electronic computer in Britain. Designed and built at the National Physical Laboratory, Middlesex in 1949-1950, it was based on plans for a larger computer (the ACE) designed by the mathematician Alan Turing (1912-1954) at NPL between 1945 and 1947. Previously Turing worked on the Colossus computer used in codebreaking at Bletchley Park during World War II. Pilot ACE was estimated to have cost £50,000 to design and build, but by 1954 had earned over £240,000 from advanced scientific and engineering work in various fields including crystallography, aeronautics and computing bomb trajectories.](https://friendica-leipzig.de/photo/preview/600/254277)
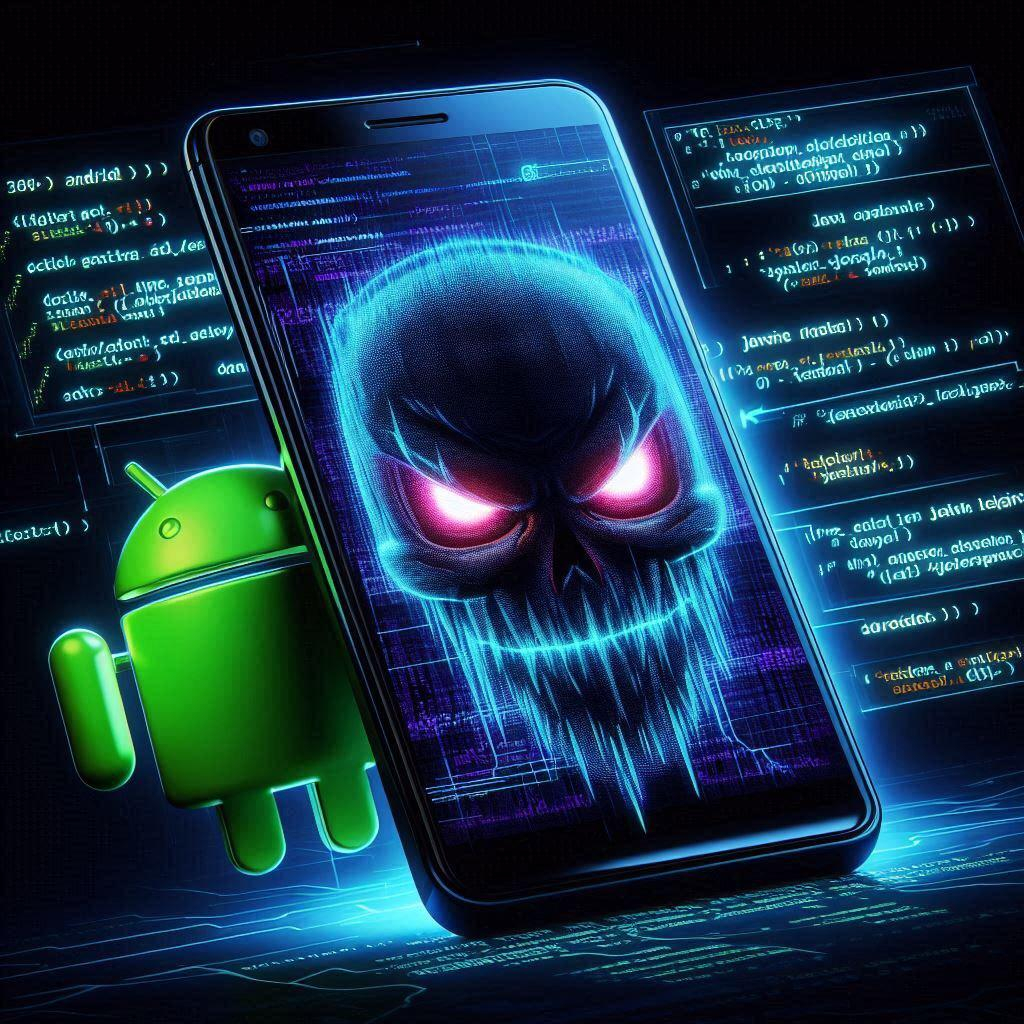




![[ImageSource: Zimperium]
Overview of latest FakeCall attacks.
The FakeCall malware typically infiltrates a device through a malicious app downloaded from a compromised website or a phishing email. The app requests permission to become the default call handler. If granted, the malware gains extensive privileges.
A fake call interface mimics the actual Android dialer, displaying trusted contact information and names, elevating the level of deception to a point that's hard for victims to realize.
What makes this malware so dangerous is that when a user attempts to call their financial institution, the malware secretly hijacks the call and redirects it to an attacker's phone number instead. [ImageSource: Zimperium]
Overview of latest FakeCall attacks.
The FakeCall malware typically infiltrates a device through a malicious app downloaded from a compromised website or a phishing email. The app requests permission to become the default call handler. If granted, the malware gains extensive privileges.
A fake call interface mimics the actual Android dialer, displaying trusted contact information and names, elevating the level of deception to a point that's hard for victims to realize.
What makes this malware so dangerous is that when a user attempts to call their financial institution, the malware secretly hijacks the call and redirects it to an attacker's phone number instead.](https://friendica-leipzig.de/photo/preview/600/227654)

![[ImageSource: Apple]
Interacting with the Private Cloud Compute client from the Virtual Research Environment.
Apple provides a Virtual Research Environment (VRE), which replicates locally the cloud intelligence system and allows inspecting it as well as testing its security and hunting for issues.
“The VRE runs the PCC node software in a virtual machine with only minor modifications. Userspace software runs identically to the PCC node, with the boot process and kernel adapted for virtualization,” Apple explains, sharing documentation on how to set up the Virtual Research Environment on your device.
VRE is present on macOS Sequia 15.1 Developer Preview and it needs a device with Apple silicaon and at least 16GB of unified memory.
<https://security.apple.com/documentation/private-cloud-compute/vresetup> [ImageSource: Apple]
Interacting with the Private Cloud Compute client from the Virtual Research Environment.
Apple provides a Virtual Research Environment (VRE), which replicates locally the cloud intelligence system and allows inspecting it as well as testing its security and hunting for issues.
“The VRE runs the PCC node software in a virtual machine with only minor modifications. Userspace software runs identically to the PCC node, with the boot process and kernel adapted for virtualization,” Apple explains, sharing documentation on how to set up the Virtual Research Environment on your device.
VRE is present on macOS Sequia 15.1 Developer Preview and it needs a device with Apple silicaon and at least 16GB of unified memory.
<https://security.apple.com/documentation/private-cloud-compute/vresetup>](https://friendica-leipzig.de/photo/preview/600/225193)
